Understanding Cell Selection in OpenFOAM: From Code to Visualization
Published:
When working with Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), we often need to focus on specific regions of our mesh for detailed analysis. OpenFOAM provides powerful tools for this purpose, but creating custom applications gives us more control over how we select and analyze these regions. In this guide, we’ll explore how to create a tool that selects cells within a specified region and visualize them effectively.
Understanding the Code Structure
Let’s examine a practical application that selects cells within a defined bounding box. Our code uses OpenFOAM’s built-in spatial searching capabilities to identify cells efficiently.
Core Components and Their Purpose
#include "fvCFD.H"
#include "argList.H"
#include "fvMesh.H"
#include "indexedOctree.H"
#include "treeDataCell.H"
#include "cellSet.H"
using namespace Foam;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
#include "setRootCase.H"
// Initialize OpenFOAM time and mesh handling
Time runTime(Time::controlDictName, args);
// Load the mesh from constant/polyMesh directory
fvMesh mesh
(
IOobject
(
fvMesh::defaultRegion,
runTime.constant(),
runTime,
IOobject::MUST_READ
)
);
This initial section sets up our OpenFOAM environment. The fvMesh object gives us access to all mesh information, which is essential for cell selection.
Defining the Search Region
// Define our region of interest using a bounding box
// The values below are selected such that our region lies in the middle of
// the domain of cavity case which has an overall domain bounding box (0 0 0) (0.1 0.1 0.01)
// This can later be implemented programmatically
scalar minX = 0.025;
scalar minY = 0.025;
scalar minZ = 0.0;
scalar maxX = 0.075;
scalar maxY = 0.075;
scalar maxZ = 0.01;
treeBoundBox searchBox(point(minX, minY, minZ), point(maxX, maxY, maxZ));
The treeBoundBox represents a rectangular volume in 3D space. Think of it as defining a box by specifying its opposite corners. Any cell that intersects with this box will be selected.
The Cell Selection Process
// Use OpenFOAM's octree for efficient spatial searching
const indexedOctree<treeDataCell>& cellTree = mesh.cellTree();
// Find all cells that intersect with our search box
labelHashSet foundCells;
label count = cellTree.findBox(searchBox, foundCells);
This section performs the actual cell selection. OpenFOAM uses an octree data structure, which divides space into increasingly smaller cubes. This makes searching for cells in a particular region much faster than checking every cell in the mesh.
Creating the CellSet
// Store our selection as a cellSet for later use
cellSet selectedCellSet
(
mesh,
"selectedBox", // name of the cellSet
foundCells // the cells we found
);
// Write the cellSet to disk
selectedCellSet.write();
A cellSet is OpenFOAM’s way of persistently storing cell selections. When written to disk, it can be used by other OpenFOAM utilities or visualization tools.
Quick Compilation Guide
- Create the application structure:
cd $WM_PROJECT_USER_DIR/applications foamNewApp whatsinthebox Replace the generated code with our cell selection code.
- Compile:
wmake - The complete code is available in my github repository
Visualization Using foamToVTK
After running your application and creating the cellSet, visualization is straightforward using the VTK format:
- Convert the cellSet to VTK format:
foamToVTK -cellSet selectedBoxThis command creates a VTK file containing only the selected cells.
- Open ParaView and load both:
- Your case’s
.foamfile for the complete mesh - The generated VTK file (
VTK/selectedBox.vtk) for the selected cells
- Your case’s
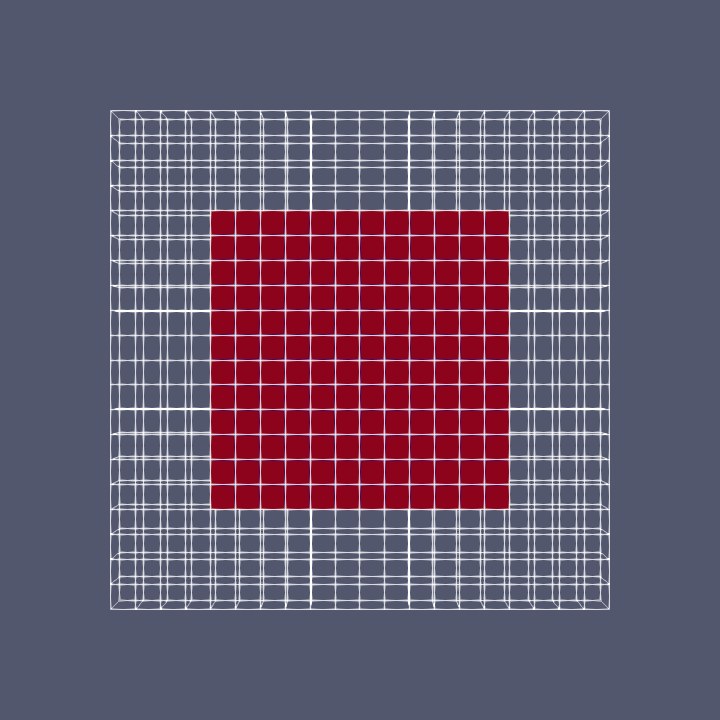
Conclusion
Understanding how to programmatically select and visualize cells is crucial for advanced CFD analysis. The combination of OpenFOAM’s powerful selection tools and VTK visualization provides a robust framework for examining specific regions of your mesh. Whether you’re debugging mesh issues, analyzing flow patterns, or preparing for advanced simulations, these tools give you the control and insight needed for effective CFD work.

Leave a Comment